Applying the Triple Bottom Line in Course Design
Try This:
Explore the the Triple Bottom Line. Can you see now how your course material is related?
The Triple Bottom Line is an Economics theory that states businesses should focus as much on the social and environmental aspects of operations as the economic dimension. In other words, profit is joined by people and planet as the drivers behind decision-making.

“The natural capital remains intact… the extraction of renewable resources should not exceed the rate at which they are renewed”, in addition, waste should not exceed the absorption capacity of the earth, “non-renewable resources should be minimized” (Sahota, 2014, p. 2).

The “cohesion of society” and working towards a common goal where individual needs such as food, shelter, health, well-being, nutrition, education and cultural expression must be met (Sahota, 2014, p. 2). Within education, inclusion and diversity is valuable to enhance learning, enabling a ‘big picture’ view (i.e., Atkas, 2015; Groulx et al., 2020; Martinez-Buján et al., 2020; Savage et al., 2015; Stephens et al., 2008) as well as to foster a sense of belonging towards change and increase engagement in learning.

The economic pillar of the triple bottom line considers whether the development towards the other two pillars, the environment and social sustainability is “financially feasible” (Sahota, 2014, p. 2). In addition to further development of financial literacy, knowledge and creating opportunities to reflect the survival needs of this generation and next generation.
Watch the following video to learn more about the “triple bottom line”:
Source: (Reproduced from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Sustainable_development.svg authored by Johann Dreo, inspired from image ‘Sustainable Development’.).
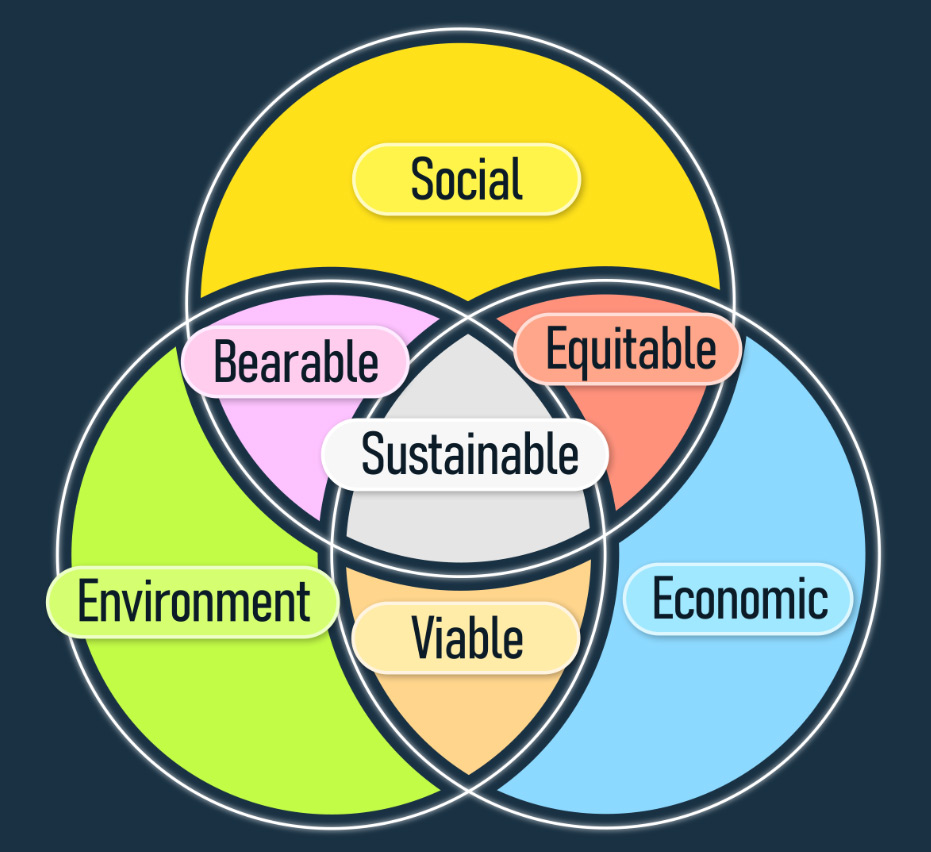
Reflect on the following Venn diagram, which reveals the outcomes when the triple bottom line is partially or completely applied. Can you think of an example or reason for each of the following prompts?
Humber College
- A triple bottom line that excludes the social aspect is considered to be viable because .
- A triple bottom line that excludes the environment is considered to be equitable because .
- A triple bottom line that excludes the economic aspect IS considered to be bearable because.
- Sustainability must include positive social, economic and environmental impacts because .