Adding Sustainability Using Rubrics
Vineyard Perspective | Shutterstock
Rubrics can help support learner development of sustainability competencies. Developing rubrics that include these skills with performance levels that evaluate the degree to which learners engage with the skills instead of how well the learners perform the skills can be more motivating and encourage learner self-reflection. Think Blooms Taxonomy or other learning taxonomies that demonstrate rigor.
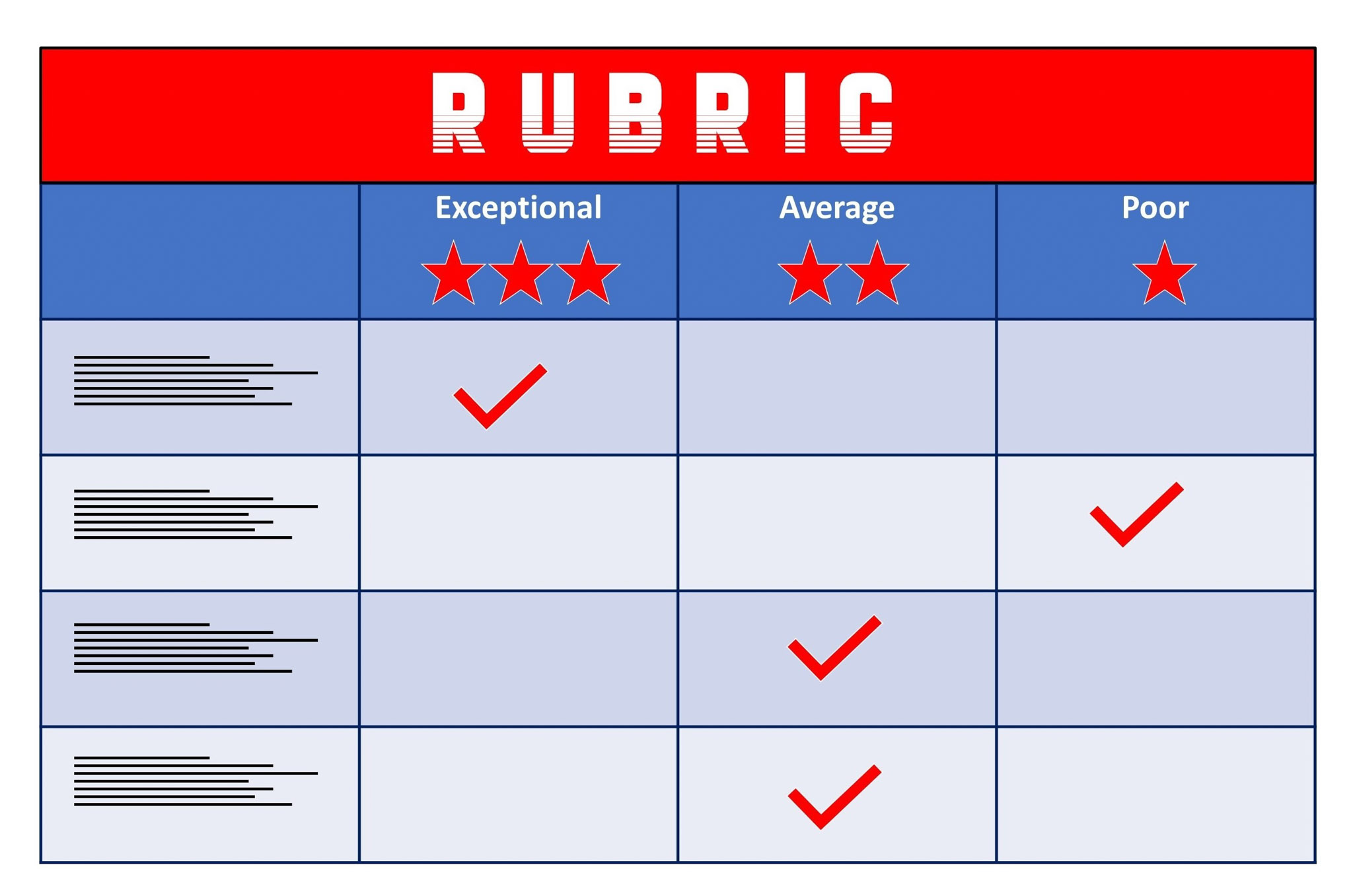
Consider the following rubric:
Able to identify qualities of strong collaboration; low participation in a group setting with limited acceptance of others’ perspectives
Able to participate actively in a group, engaging in active listening and receptive of different perspectives
Able to lead a group, engaging in active listening and adapting collaboration style to be inclusive of different perspectives and encourage others to contribute
Recognizes importance of systems
Able to create basic systems maps, feedback loops, iceberg diagrams to help create solutions to problems
Uses systems thinking not only as a tool to help problem-solving but also as a mindset that is embedded in everything they do
This rubric, focusing on sustainability competencies, may not assess student knowledge of sustainability as a concept, but it helps learners recognize the skills they are learning and also what they need to do in order to deepen their mastery of them.
To look at another example, proceed to the next page.